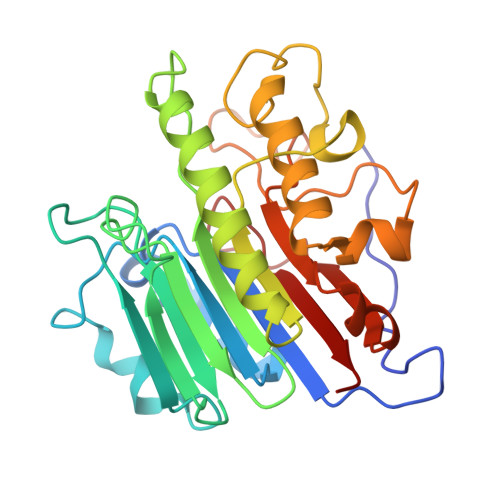
APE1 active site residue Asn174 stabilizes the AP site and is essential for catalysis.
DeHart, K.M., Hoitsma, N.M., Thompson, S.H., Borin, V.A., Agarwal, P.K., Freudenthal, B.D.(2025) J Biological Chem 301: 110655-110655
- PubMed: 40902980
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110655
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9DP1, 9DP2, 9DP3, 9DP4 - PubMed Abstract:
Apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites are common and highly mutagenic DNA lesions that can arise spontaneously or as intermediates during base excision repair. The enzyme apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) initiates repair of AP sites by cleaving the DNA backbone at the AP site via its endonuclease activity. Here, we investigated the functional role of the APE1 active site residue N174 that contacts the AP site during catalysis. To do so, we rationally designed four APE1 mutants (N174A, N174D, N174Q, and N174K) that altered the hydrogen bonding potential, electronegativity, and side chain length of residue 174. Kinetic analysis determined that AP site cleavage was impaired in our APE1 N174A , APE1 N174D , and APE1 N174K mutants, but not in our APE1 N174Q mutant. Using X-ray crystallography and molecular dynamic simulations of our APE1 mutants, we attributed the poor cleavage of our APE1 N174A and APE1 N174D mutants to lack of hydrogen bonding between residue 174 and the AP site. From these experiments, we also discovered that the altered charge of residue 174 in APE1 N174D and APE1 N174K mutants contributed to impaired cleavage. From analysis of our mutants, we determined that in APE1 WT , N174 stabilizes AP DNA within the APE1 active site via hydrogen bonding promoting cleavage of AP sites. We also found that the neutral charge of N174 in APE1 WT contributes to an optimal electrostatic environment during the APE1 endonuclease reaction resulting in efficient AP site cleavage. Cumulatively, we demonstrate the importance of N174 in APE1's function and provide new insights into the molecular mechanism by which APE1 processes AP sites during DNA repair.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, Kansas, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: